DIPHTHERIA|ICDS Supervisor Kerala Study Materials
DIPHTHERIA
Diphtheria is a common infectious
disease in India.
There are reports to indicate
that the prevalence of diphtheria (number of cases of diphtheria in the
community) is on the rise in the country.
An analysis of admissions to
Infectious diseases hospital in Delhi indicates that about 13 per cent
cases of diphtheria, among the
children under five years of age, end in deaths.
The death rate due to diphtheria
is also reported to be high.
Unfortunately, it is difficult to
obtain accurate information about the actual extent of diphtheria
in warm climate countries like
India because bacteriological confirmation of the disease is not easily
available.
What Causes Diphtheria?
Diphtheria is caused by Cornye bacterium
diphtheriae, a non-motile (not moving) organism. The organism produces a
powerful toxin.
Three types of diphtheria,
bacilli are differentiated.
Gravis: Causing serious type of disease and generally accounts for about a fourth of the cases of diphtheria.
Mitis: Causing milder type of
infection contributing to about 65 per cent of the cases.
Intermedius: This accounts for
about 10 per cent of the cases.
Who can Get the Diphtheria Disease?
Age: Diphtheria is primarily a disease of children under 15 years of age. You would rarely come across cases of diphtheria in children below the age of 6 months.
The highest number of cases are observed among preschool children i.e., 1-5 year old children.
It can also occur in unimmunised
adults.
Sex: It affects both the sexes
equally.
Season: Cases of diphtheria are reported in all the seasons. But, higher numbers of cases are reported during August to October.
How Does Diphtheria Spread?
Diphtheria spread usually by contact with a patient or a person having in apparent infection (with out an recognisable clinical sign or symptom).
The transmission is through
droplet infection or infected dust.
It can also be transmitted if raw
milk contaminated with discharges from the patients is consumed.
However, in India where milk is
invariably boiled before consumption transmission by milk is not likely to
occur.
It is rare to contract the
disease by handling articles soiled with discharges from lesions of infected
persons.
The organism can sometimes enter
through wounded skin and lead to infection.
Incubation period: Usually 2 to 5
days.
Period of Communicability: The
disease can spread from an infected person to another unimmunised person as long
as the virulent bacilli are present in the discharges of the lesions.
Generally, it is communicable for
about 2 weeks but never for more than 4 weeks.
Susceptibility: Infants born to
mothers who are immune do not get the disease during the first six months of
their life.
Recovery from an attack of
diphtheria is not followed by long lasting immunity as in the case of measles.
Prolonged active immunity can be
induced by giving diphtheria toxoid.
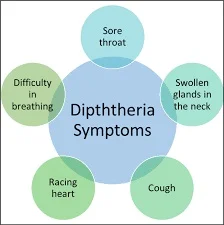
SYMPTOMS AND COMPLICATIONS of Diphtheria
Diphtheria is an acute
communicable disease which affects the nose, throat and tonsils.
The bacilli multiply at the site of
implantation (insertion into the body), be it throat, nose or tonsils. It
produces local lesions at the site of implantation.
This lesion is characterised by
formation of a patch or patches of greyish false-membrane on the affected
parts such as tonsils or larynx
(voice box).
It also produces an offensive and
strong odour. There will be redening and swelling of the surrounding tissues.
The throat is moderately sore
when diphtheria affects tonsils, with swelling of the cervical lymph glands
(lymph glands in the neck region).
This may result in bull-neck appearance.
Diphtheria affecting larynx is
serious particularly in infants and children. Most often it leads to death of
the affected.
Nasal diphtheria (of nose) is
usually a mild condition marked by one sided discharge in the nose.
PREVENTION AND MANAGEMENT of Diphtheria
Immunisation: The only effective way of preventing the disease is by active immunisation by diphtheria toxoid to general population.
It is given as DPT or triple antigen along with immunisation for whooping cough and tetanus.
Three intramuscular injections of
0.5 ml each at intervals of 4 to 6 weeks are given to children at third, fourth
and fifth months of life.
A booster is given one year after
the third injection is given. For children over the age of six years, only
DT containing diphtheria and
tetanus toxoids, is given.
Identification of susceptible cases : There is a test to find out individuals who are susceptible to diphtheria.
This test is known as Schick test. This test can also be used for confirmation of successful
immunisation.
The test is an intradermal (injection into the
layers of skin) test.
A measured amount (0.2 ml) of Schick test
toxin is injected into the skin of the forearm.
Toxin inactivated by heat is
injected into the opposite arm which is called control arm.
In other words the individual has
enough antitoxin to neutralise the toxin and fight the disease.
The test is positive if red
flushing (colouring) of 1 to 5 cm diameter-appears within 1 to 2 days of
injection.
The control arm shows no change.
This would mean that the person is susceptible to diphtheria.
The community, particularly the
parents of young children, should be encouraged through education to get their
children immunised against diphtheria along with the whooping cough and
tetanus.
Sure prevention is better than
cure. But if an individual is suffering from diphtheria, how to manage such a
patient.
Management of diphtheria : In all
the cases suspected of having diphtheria, antitoxin should be administered without
waiting for bacteriological confirmation.
After comlpetion of tests for allergy to the
antitoxin , intramuscular administration of antitoxin is recommended.
Penicillin and Erythromycin are
effective but should be given along with the antitoxin.
When there are cases of
diphtheria, you should immediately take steps to arrange for injections of
antitoxins to the patients.
In other words, these patients
should be taken to the nearest hospital at the taluq or district level.
The hospital authorities will
arrange for laboratory investigations and antibiotic cover.
Simultaneously, the close
contacts in the family should be investigated and kept under watch thoroughly.
It is a sound practice to administer 500-1000 units of diphtheria antitoxin to household
contacts and others who have been in recent contact with cases of diphtheria.
POINTS TO REMEMBER on Diphtheria
Diphtheria is an acute
communicable disease affecting the nose, throat and tonsils.
Diphtheria is caused by
cornyebacterium diphtheria.
Diphtheria is primarily a
disease of children under 15 years of age.
Transmission of diphtheria is
through droplet infection or infected dust.
The throat become sore when
diphtheria affects tonsils and there is swelling of the cervical lymph glands.
Immunisation is the most
effective way of preventing the disease.
Read Also: Malaria |ICDS Supervisor Kerala Study Materials
Read Also:
ICDS Supervisor Questions and Answers
Common Health Problems in India & Different Levels of Health care in India
1. Meal Planning for the Infant
2. Spplementary foods for Infants
4. How to Feed Infant? Meal Plan for Infants
5. Meal Planning for the Prechoolers
Topic wise Notes for ICDS Supervisor Exam
3. Psychology
4. Physiology
5. Microbiology
6. Sociology
MCQ Questions & Answers for ICDS Supervisor
2. Previous Questions MCQ|ICDS Supervisor Exam|ICDS Supervisor Kerala PSC (1-20)
3. Previous Questions MCQ|ICDS Supervisor Exam|ICDS Supervisor Kerala PSC (21-30)
13. ICDS Supervisor Previous Questions Set 1
14. ICDS Supervisor Previous Questions Set 2
15. ICDS Supervisor Previous Questions Set 3
16. ICDS Supervisor Previous Questions Set 4
17. ICDS Supervisor Previous Questions Set 5
18. ICDS Supervisor Previous Questions Set 6
19. ICDS Supervisor Previous Questions Set 7
20. ICDS Supervisor Previous Questions Set 8
21. ICDS Supervisor Previous Questions Set 1
22. Elementary Care & Education MCQ
23. Solved Previous Question Paper ICDS Supervisor
24. Women & Child ICDS Supervisor Exam
25. Extension Education Notes for ICDS Supervisor
26. Complete NOTES Child Psychology
Nutrition Notes
More Topic wise Notes can be got from the Website https://www.previousquestions.in
To Join Telegram, Click Here
Check These also
Job News
Exam Preparation
Exam Preparation
Download printable OMR Sheet PDF for practice
ബിഹേവിയറിസം
ഗസ്റ്റാള്ട്ടിസം Gestaltism Learning methods
ജ്ഞാതൃവ്യവഹാരവാദം ( Cognitive behaviorism)
ജ്ഞാതൃവാദം (Cognitivism)
നാഡീമന:ശാസ്ത്രം (neuropsychology)|പഠനത്തെ സ്വാധീനിക്കുന്ന ഘടകങ്ങള്
വ്യക്തിത്വം Personality
PART 2 ഉള്പ്പെടുത്തിയുളള വിദ്യാഭ്യാസം Inclusive education
ദിനാചരണങ്ങള് Important dates based on themes






![[Set 3] MCQ for ICDS Supervisor Exam|ICDS Supervisor Kerala PSC](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEirmpde6UGlx94eDLtWkrJ18PAc_d8GVw_K-4E1izTltkjugPJEyBVplbm_S85f0gxNowfcbT6afCPnAjTF0_TKYK9Lq7zm1fnQU-TPsKEosx0opg5d05b-nry5qBPrKUZMoVD7BOFpW-5jxoAlMCTysmHKi30ieam3tPtA_ohH_Z5D2Uu1PPxt-qZ38wY/s72-c/icds-supervisor-mcq.jpg)

![[Solved paper]Assistant Engineer Agriculture Kerala PSC Previous Question Paper|Assistant Engineer Agriculture Kerala PSC Question paper 665/2022](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEiE5XMCyjBp5qgQ6gc1f5YxnObTDPt4ioa1TM0DhzIzBsKfJUJZg1nhfOcliABQCpnIj9INlw2xliBzlEEPCd_tgUhxvJhySogAkZFGKaWZ9GujHt4KwM-DSmOLBbLLlexxurubFQobMSgo11YP_2eVKCTrV0CWiwOlouEr1abUj5m6V5fJomuMxLK5U5o/s72-w640-c-h360/Assistant%20Engineer%20Agriculture%20Kerala%20PSC%20Previous%20Question%20Paper.jpg)
